15358968703

Basic knowledge about continuous pipe mills
What is a continuous rolling mill?
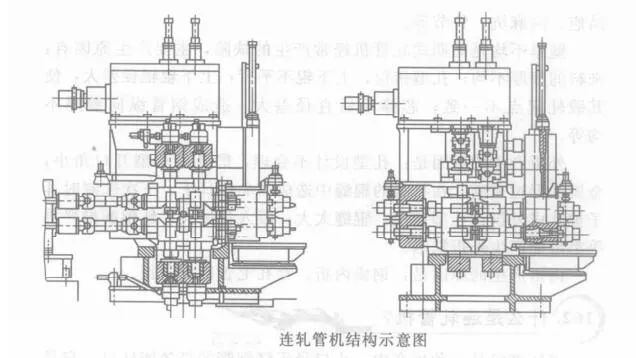
Continuous tube rolling mill is a high-efficiency rolling mill for producing medium and small diameter seamless steel tubes. It is to sleeve the perforated capillary on a mandrel, and pass through 5 to 9 consecutively arranged two-roll mills with the axes of the rolls between the adjacent two stands perpendicular to each other and the stand spacing is close. The capillary is longitudinally rolled. The structure of the continuous rolling mill is shown in the figure below. Because the continuous rolling mill can achieve large deformation, generally the total deformation rate can reach 80%, and the elongation coefficient is 3.5 to 5, so it has high productivity. The modern continuous rolling mill is equipped with a tension reducer. Usually, the continuous tube mill only needs to produce one or two diameters of steel pipes, and then the tension reducer is used to expand the range of varieties.
Classification and process characteristics of continuous tube rolling mills
According to the different ways of mandrel movement, continuous tube rolling mills can be divided into three types: full floating, limited and semi-restricted mandrel continuous rolling mills.
(1) The technological characteristics of the fully floating mandrel continuous pipe rolling mill are as follows. In the rolling process of the fully floating mandrel continuous pipe rolling mill, the mandrel rod freely passes through the rolling mills, and then the mandrel rod is extracted from the steel pipe by the stripping machine. Since the speed of the mandrel bar is not controlled during the rolling process, the movement speed of the mandrel bar changes many times during the whole rolling process, which will lead to changes in the metal flow conditions, which will directly affect the deformation process and cause fluctuations in the longitudinal wall thickness and diameter of the steel pipe. Thus affecting the dimensional accuracy of the finished pipe. In addition, the length of the mandrel is large, which increases the cost and difficulty of manufacturing. On the other hand, when rolling a steel pipe with a large diameter, the long mandrel has a large mass, and the steel pipe runs on the roller table with an excessively heavy mandrel, which will cause The damage of the steel pipe also brings great difficulties to the maintenance and storage of the mandrel. Therefore, at present, the full-floating mandrel rolling mills are all used for the production of small and medium-sized steel pipes with a steel pipe diameter of less than 177.8.
(2) The technological characteristics of the stop mandrel continuous rolling mill are as follows. Restricted mandrel continuous pipe rolling mill controls the mandrel during the whole rolling process, so that the mandrel runs at a set constant speed lower than the rolling speed. After the rolling process, the steel pipe is released from the mandrel, and the mandrel is quickly returned by the stopper mechanism. Practice has proved that the moving speed of the mandrel should be higher than the bite speed of the first rolling mill and lower than the exit speed of the first rolling mill. In this way, the movement speed of the core holder is lower than the rolling speed of all the stands during the whole rolling process, thereby avoiding the irregular metal flow which leads to the change of the rolling conditions. Due to the limited movement speed of the mandrel, the rolling pressure of each stand is relatively lower than that of the full-floating mandrel rolling mill, the metal flow shows a certain regularity, the elongation coefficient can be larger, and the Obtain very good tube wall thickness tolerances to achieve the effect of improving production and quality. Moreover, the length of the mandrel can be shortened, and large and medium-sized steel pipes can be produced.
(3) The technological characteristics of the semi-restricted mandrel rolling mill. The semi-restricted mandrel rolling mill also controls the speed of the mandrel during the rolling process, but the mandrel is released before the end of the rolling process, and the mandrel is taken out of the rolling mill like a fully floating continuous rolling mill, and then Then, the mandrel is pulled out from the steel pipe by the de-rod machine. In recent years, the semi-restricted mandrel rolling mill has begun to receive attention. The tube is at the back, and the mandrel bar is released after the rolling mill is rolled out. During the rolling process, it has the technological characteristics of the mandrel rolling mill with limited movement, and can reduce the rolling cycle time, and can roll 4 steel tubes per minute. . It can be considered that the semi-restricted mandrel rolling mill is a promising model to replace the full floating mandrel rolling mill. The length of the mandrel is much shorter than that of the full-floating type, but slightly longer than that of the limiting mandrel, but it is still limited by the de-rod condition, and the mandrel is too heavy.
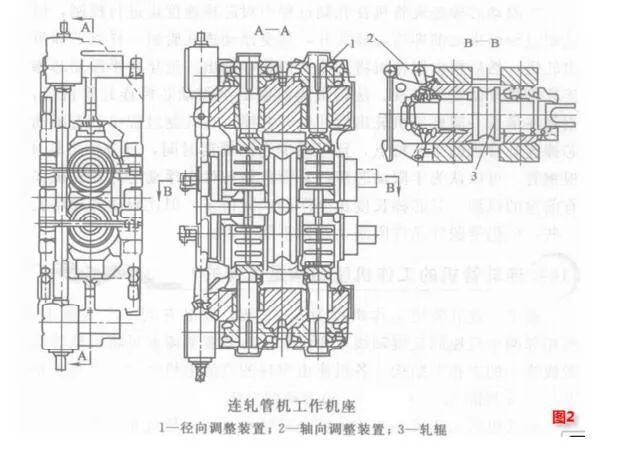
The structure of the working stand of the continuous rolling mill
Usually, there are 5 to 9 working stands of a continuous rolling mill, which are installed on the same base, and the axes of the rolls between every two adjacent stands are perpendicular to each other. For the sake of compact arrangement, the rack archway is made into a unified square box-shaped structure. Each stand is driven by a separate DC motor, arranged horizontally, and drives two rolls through a conical-cylindrical gearbox. The working stand of the pipe rolling mill is essentially a single-hole type two-high rolling mill (Fig. 2). Both ends of the rolls are equipped with rolling bearings and have manual radial adjustment devices. The rolls use spring balance devices and lever-type axial adjustment devices. Generally, the diameter of the continuous rolling mill is ¢400~SOOmm, and the length of the roll body is 220~300mm.