15358968703

Discussion on oxidation of billet in heating furnace
Abstract: in this paper, the mechanism, causes and influencing factors of iron oxide scale formation during + billet heating in the heating furnace are briefly discussed, and some measures and methods to reduce oxidation burning loss are put forward.
Key words: billet, heating furnace, oxidation
1. Foreword
The oxidation of steel billet means that the surface of steel billet is reacted by the gas in the heating furnace (such as CO2, H2O ↑, O2, SO2) to form iron oxide scale (i.e. burning loss). The percentage of iron oxide scale in the total amount of heated billet is called burning loss rate. Under normal circumstances, the one-time burning loss rate of steel heating is about 1%-1.5%, serious can reach 3%, and better can be controlled below 1%.
The oxidation of billets not only greatly reduces the yield, but also has the following adverse effects:
(1) The accumulated iron oxide scale in the furnace absorbs a large amount of heat, which reduces the thermal efficiency of the heating furnace and the heating speed of the billet;
(2) After melting, the iron oxide will erode the refractory bricks, which will reduce the service life of the heating furnace. If it is serious, the furnace has to be shut down in advance for overhaul;
(3) In the process of smoke exhaust, due to adsorption, the iron oxide scale will enter the regenerator or with the flue gas, which will cause the heat storage ball to harden and shorten the service life of the heat storage ball after melting in case of heat. At the same time, the iron oxide scale will block the small hole of the layer brick or the small hole of the heat storage body in the regenerator. All these will lead to serious consequences, such as poor exhaust of heating furnace, increase of furnace pressure, difficulty in heating up, etc;
(4) The cleaning of iron oxide increases the labor intensity of production workers and increases the costs of energy, transportation and secondary recycling;
(5) The production of iron oxide scale will also increase the wear of rolls and affect the surface quality of finished products.
In a word, the oxidation of billet is harmful but not beneficial. So, what are the factors that affect billet oxidation? How to effectively inhibit the oxidation of billets?
2. Mechanism and necessary factors of iron oxide formation
The oxidation of steel billet is the result of chemical reaction between oxygen atom and iron atom during the heating process of steel billet in the heating furnace. During the heating process of the billet, the oxygen atoms in the furnace gas diffuse to the interior of the billet through the billet surface. When the two elements contact, a chemical reaction will occur under certain conditions to form iron oxide. The outermost layer of iron oxide is Fe2O3, the middle is Fe3O4, and the inner layer is FeO.
(1) Heating temperature.
Relationship between furnace temperature and billet oxidation
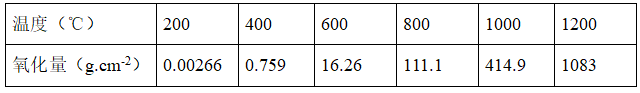
(2) Heating time: the longer the heating time of the billet, the more serious the oxidation of the steel and the more iron oxide scale is generated. Therefore, reducing the residence time of the steel at high temperature is an important measure to reduce the oxidation loss. This requires the heating workers to "contact frequently" during the operation, reasonably adjust the furnace temperature according to the waiting time for rolling, and strictly follow the relevant cooling system of the heating furnace, so as to eliminate the phenomenon of long-term insulation under high temperature. In addition, increasing the temperature and shortening the heating time of the billet can also reduce the oxidation. After the billet is fired at 600 ℃, the oxidation amount can be reduced by half; It can be seen from the above table that the higher the heating temperature, the more intense the oxidation. At 600-700 ℃, the billet begins to form iron oxide scale; When the temperature is 900-1000 ℃, the oxidation rate is accelerated and the iron oxide scale becomes thicker; When the steel temperature is higher than 1200 ℃, the oxidation rate is 10 times that of 800 ℃. Therefore, preventing the steel from heating at high temperature is an important measure to reduce the billet oxidation.
(3) Composition of furnace gas. The composition of furnace gas also has a great influence on the oxidation of steel. The thicker the oxidizing atmosphere, the more intense the oxidation of steel, and the more iron oxide scale is generated. SO2, O2 and H2O are the most oxidizing. This requires us to frequently drain the water from the gas header to minimize the water content in the gas. During the heating process, ensure that the furnace pressure is slightly positive, and eliminate the phenomenon of negative pressure (cold air absorption); Ensure the sealing of the heating furnace, adjust the air coal ratio according to the calorific value of the gas, and try to reduce the oxidation of the billet by the surplus air;
(4) Chemical composition of steel. When chromium, nickel, silicon, manganese and other elements are contained in the steel, they will form a very dense oxide film after oxidation, which will prevent the outward diffusion of metal atoms and the inward diffusion of oxygen atoms, thus reducing the oxidation rate of the billet.
3. Measures to reduce billet oxidation
From the above analysis, it can be seen that the main measures to reduce billet oxidation are:
(1) Control the heating temperature of steel;
(2) Rapid heating is adopted to reduce the residence time of steel at high temperature;
(3) Try to adopt the hot charging method of steel billets, increase the furnace temperature of steel billets, so as to shorten the heating time of steel billets;
(4) Put an end to the phenomenon of long-time heat preservation under high temperature;
(5) Adjust the appropriate air coal ratio according to the change of gas calorific value. On the premise of ensuring the full combustion of coal gas, the excess air coefficient shall be controlled to the maximum extent and the suction of cold air shall be reduced.
(6) The condensate in the gas header shall be discharged frequently to minimize the moisture content in the gas.
As long as the above points are well controlled, the oxidation of billets will be greatly improved.